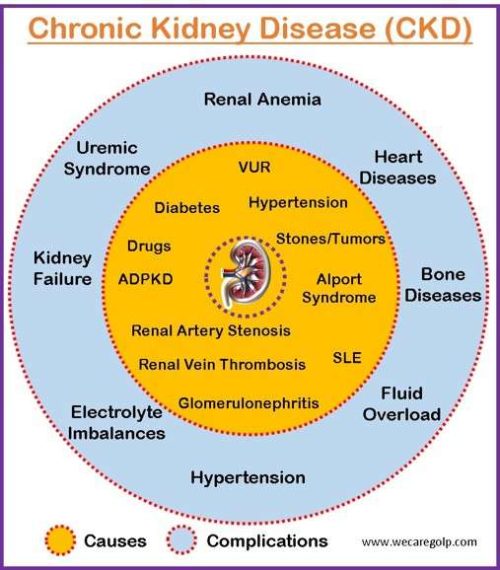
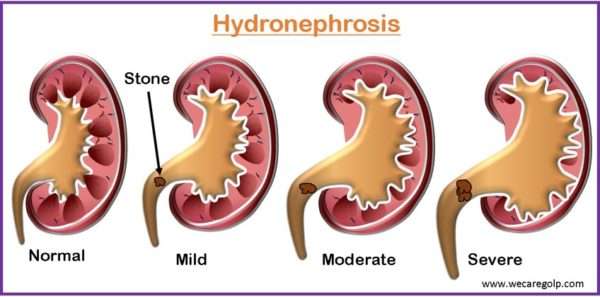
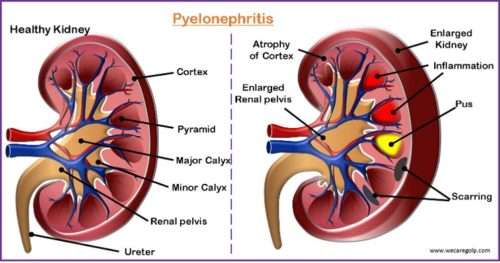
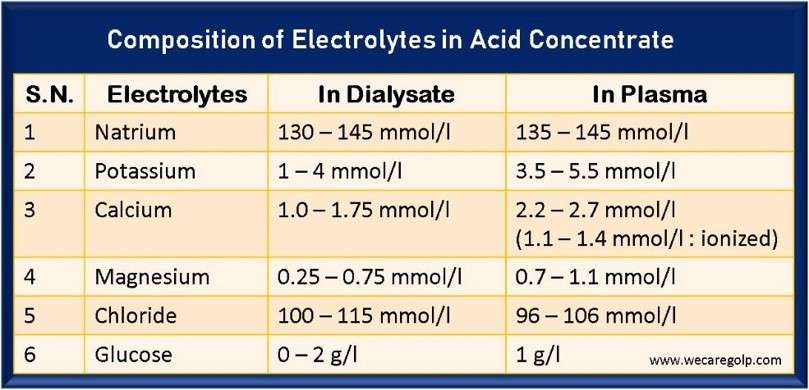
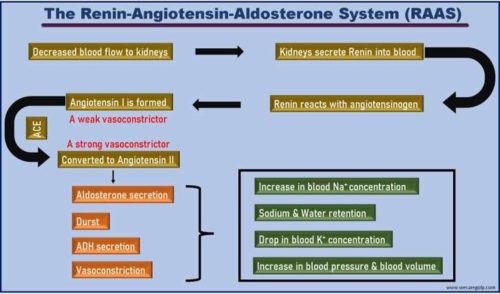
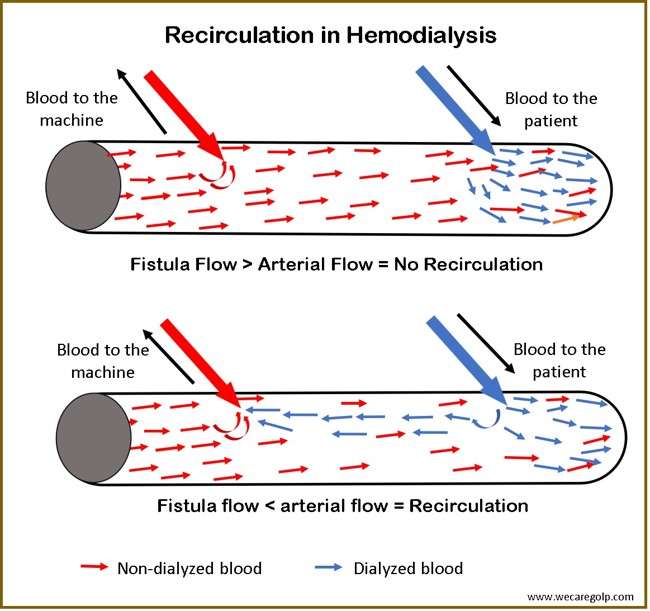
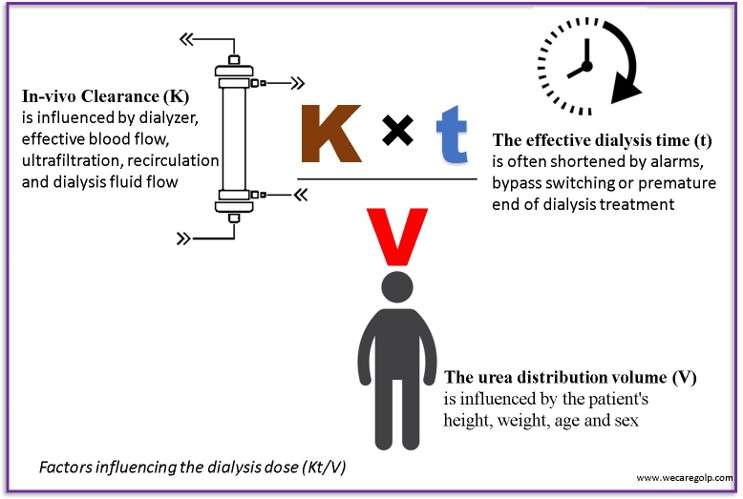
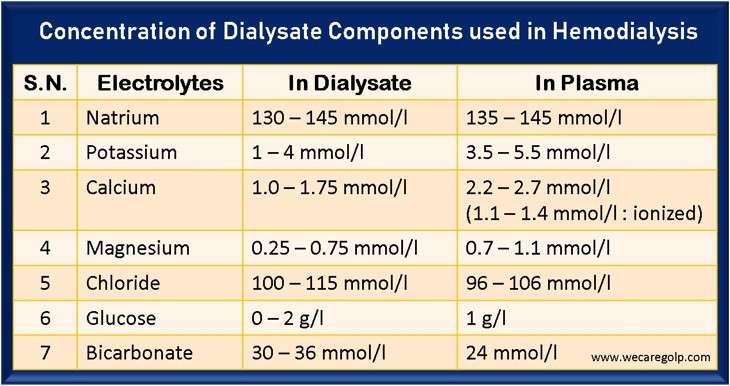
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Introduction Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a long-term disease marked by gradual and permanent kidney deterioration that impairs kidney function over time. Incidence Classification of Chronic Kidney Disease The classification of CKD is based on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and the amount of proteinuria, and it aids in the risk stratification of patients. … Read more