Myasthenia Gravis (MG): Symptoms, Management
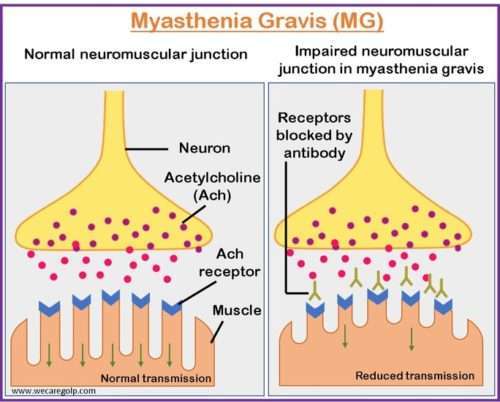
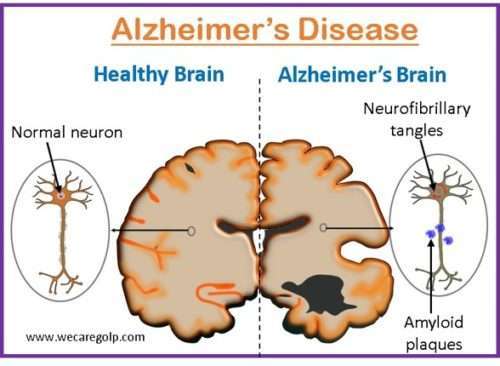
Introduction Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an acquired, rare autoimmune disorder caused by antibody-and cell-mediated destruction of acetylcholine receptors and blockade of neuromuscular transmission that results in episodic skeletal muscle weakness and easy fatigability. The autoimmune attack occurs when autoantibodies are produced against the nicotinic acetylcholine postsynaptic receptor (neurotransmitter-gated ion channel) at the neuromuscular junction of … Read more