Post-Transplant Erythrocytosis (PTE)
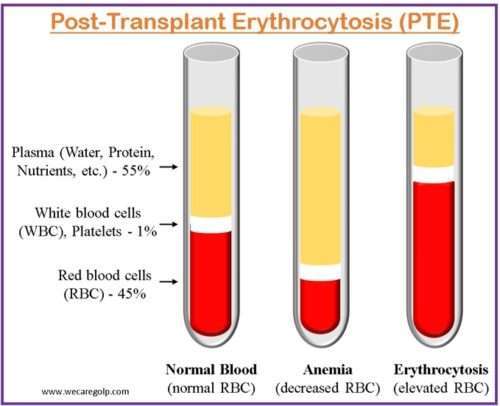
Introduction Post-transplant erythrocytosis (PTE) is defined as elevated hemoglobin (Hb) levels greater than 17 g/dL or hematocrit (Hct) levels greater than 51% for more than six months in the absence of thrombocytosis, leukocytosis, or another probable source of erythrocytosis following kidney transplantation. Erythrocytosis, also called polycythemia, is a disorder of red blood cells that occurs … Read more