The Acid Concentrate in Bicarbonate Dialysis
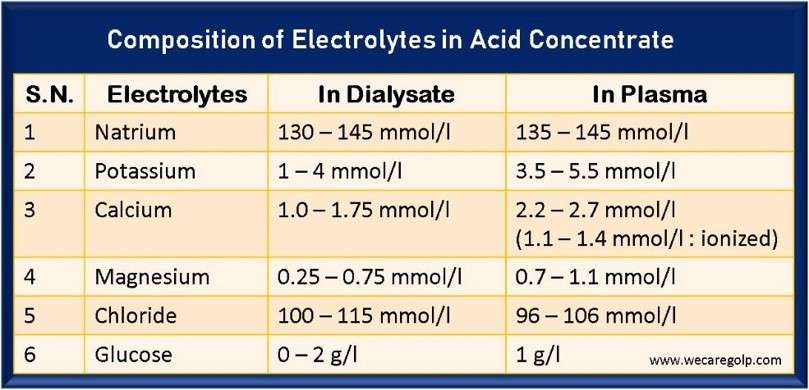
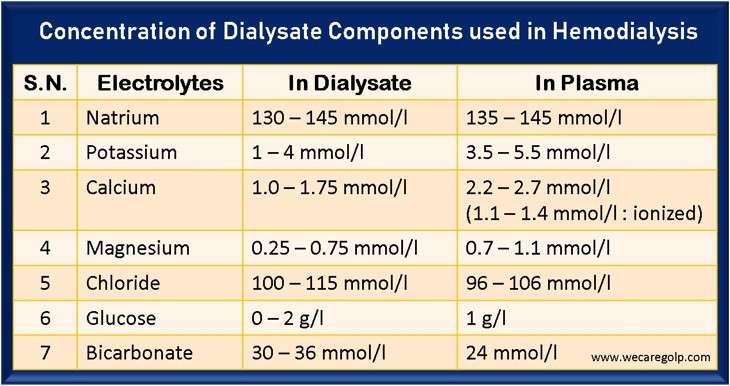
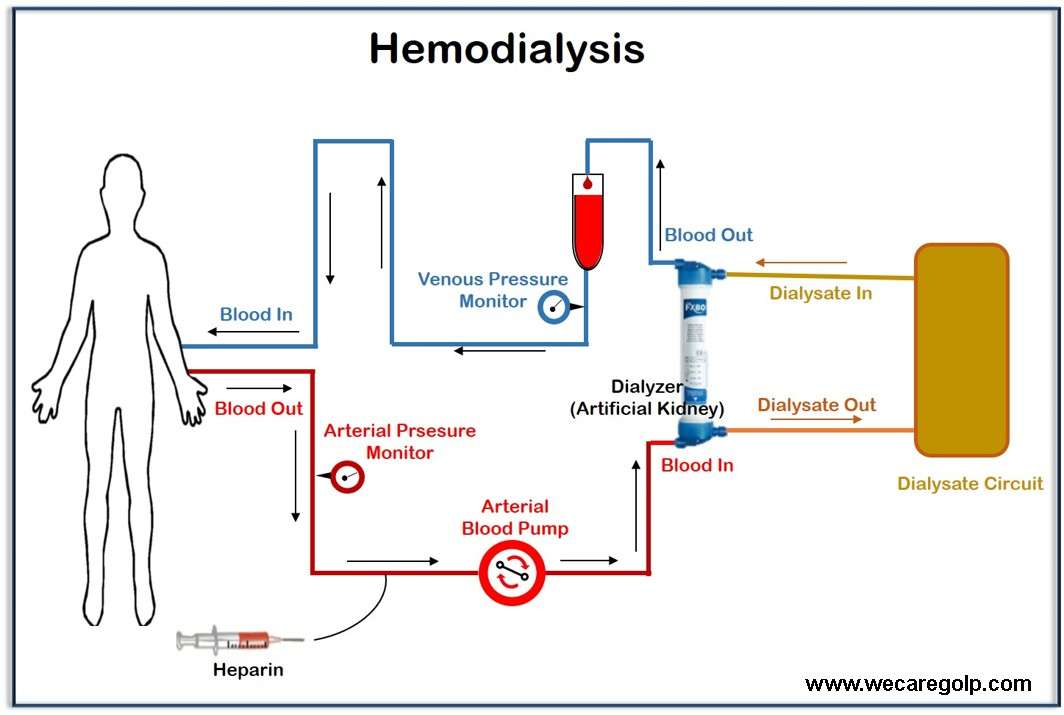
The Acid Concentrate in Bicarbonate Dialysis The acid concentrate is vital in bicarbonate dialysis. Due to the diffusion of dissolved substances from the blood into the dialysis solution and vice versa, the blood concentrations can be increased, decreased, or kept constant. Sodium Sodium significantly influences the volume and osmolarity of the extracellular fluid. Therefore, sodium … Read more