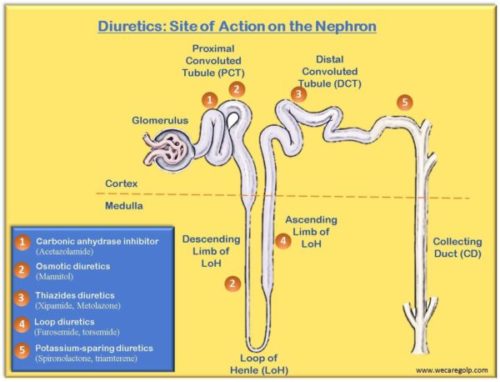
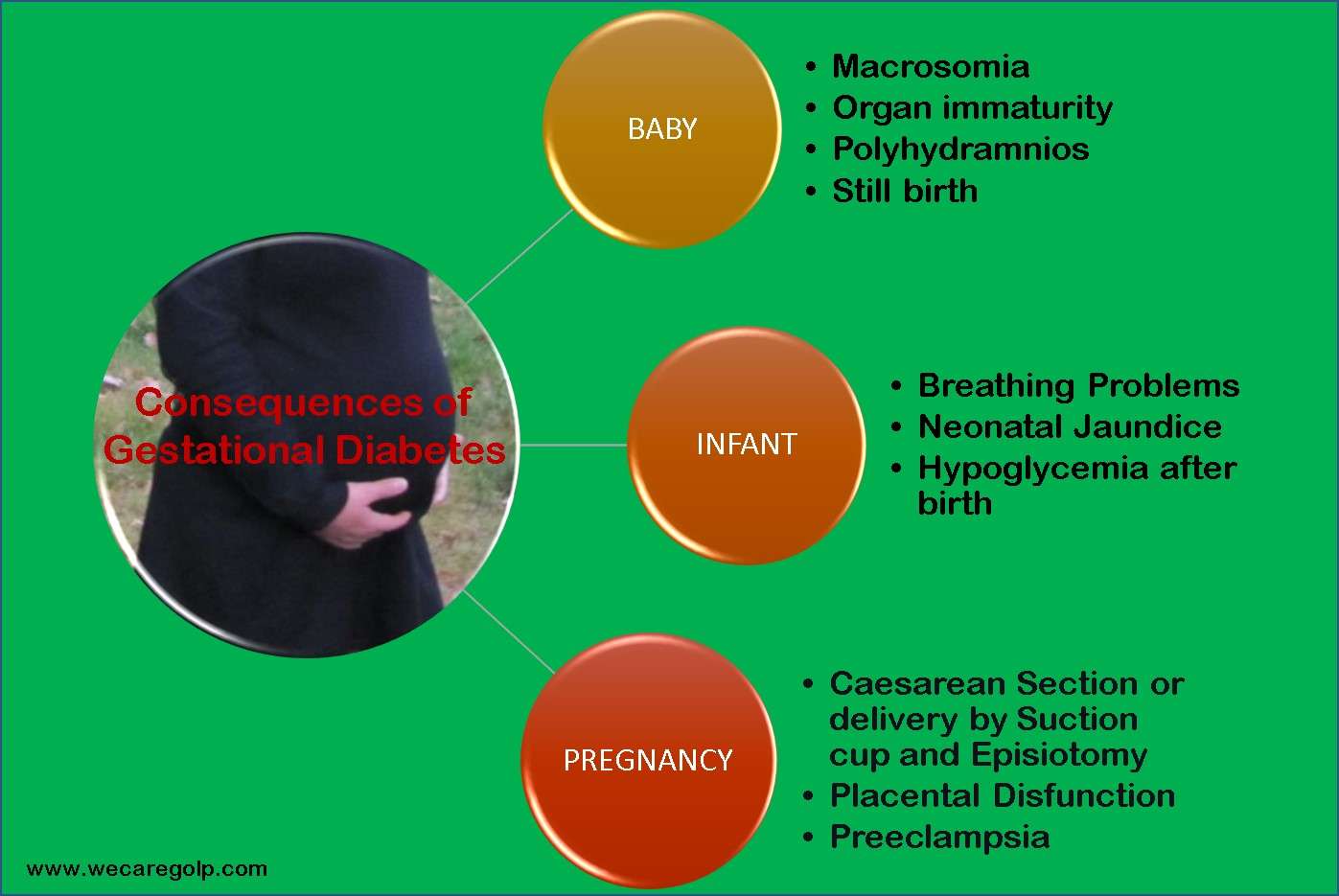
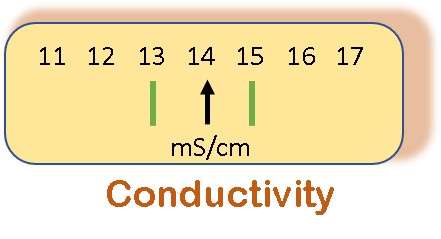
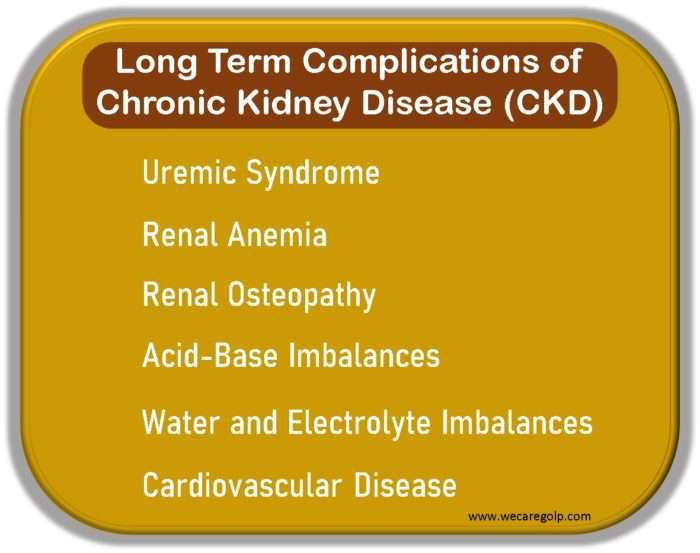
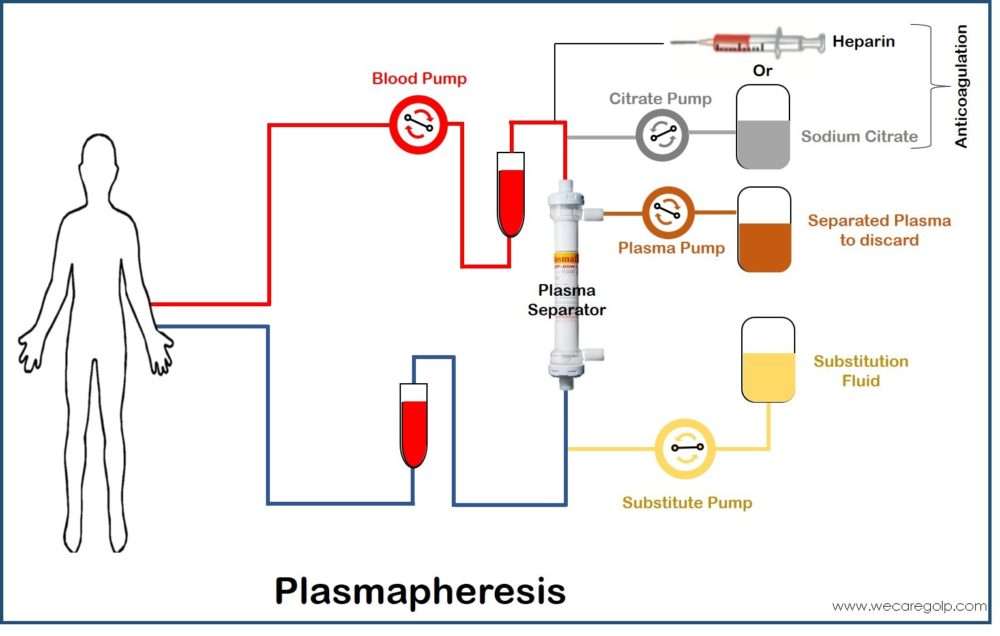
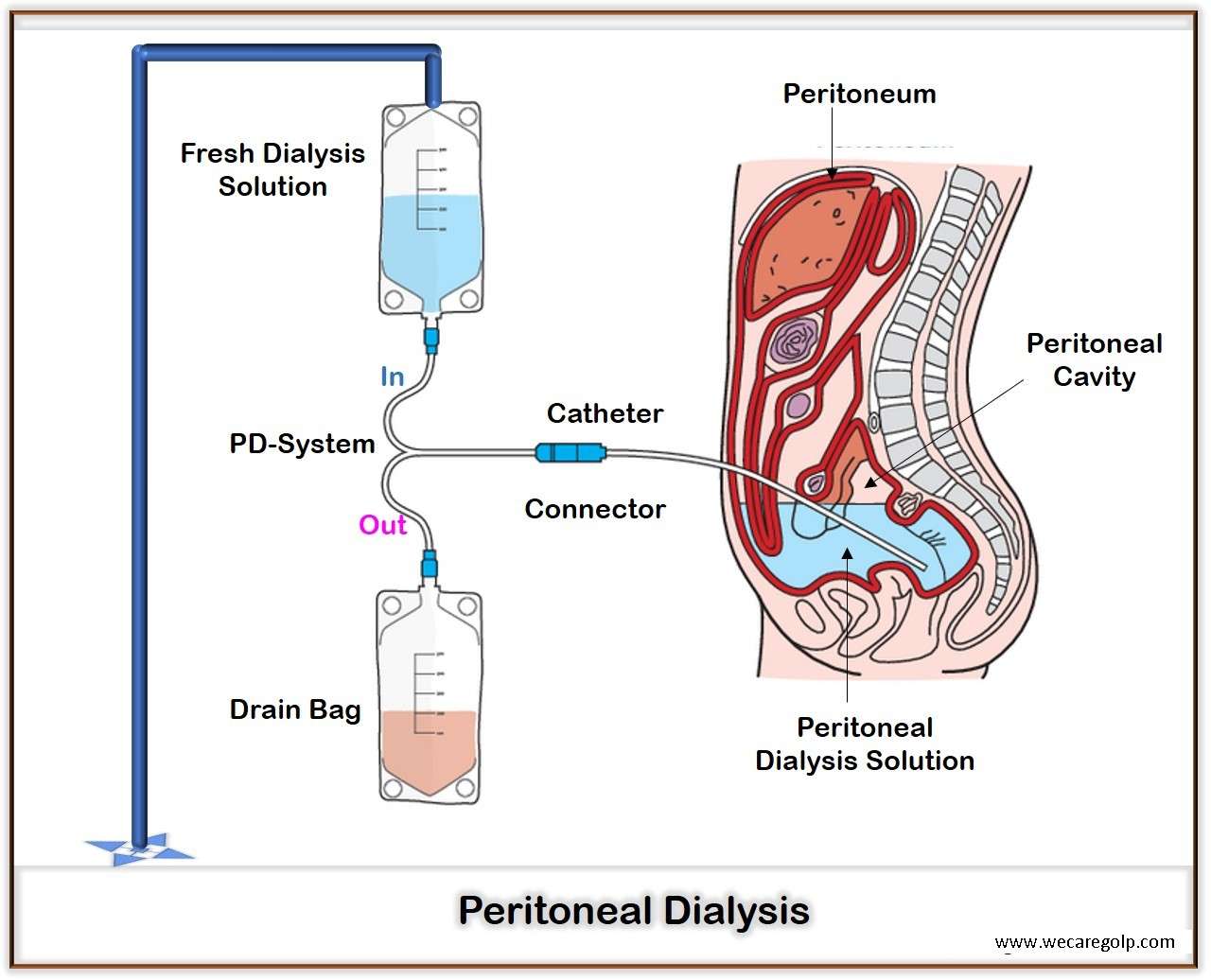
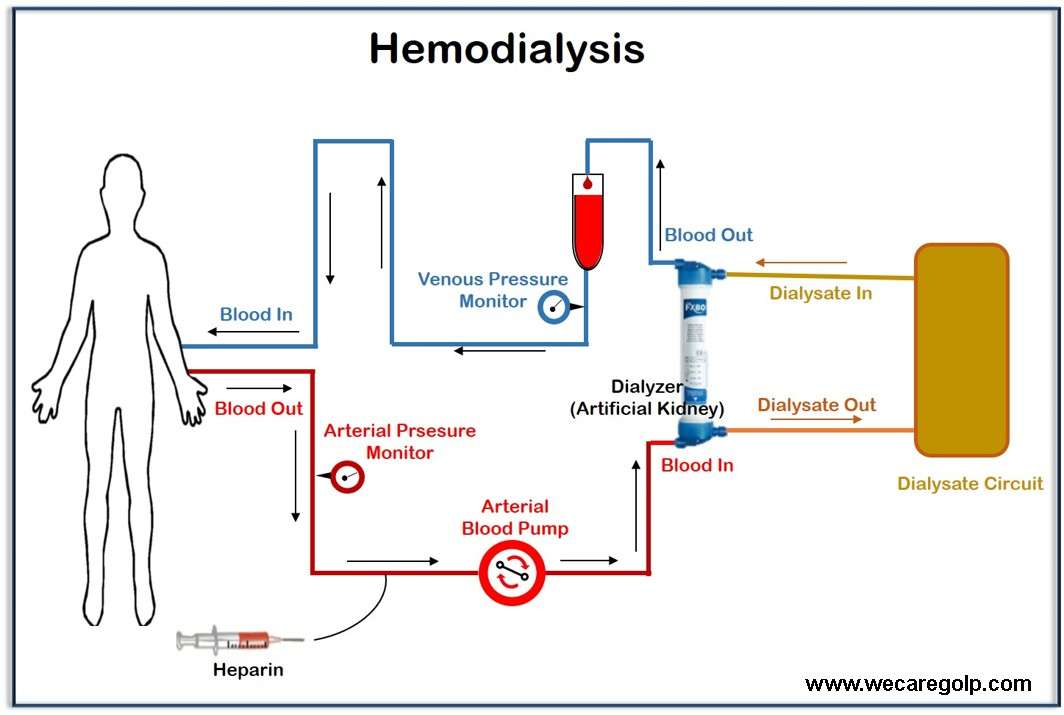
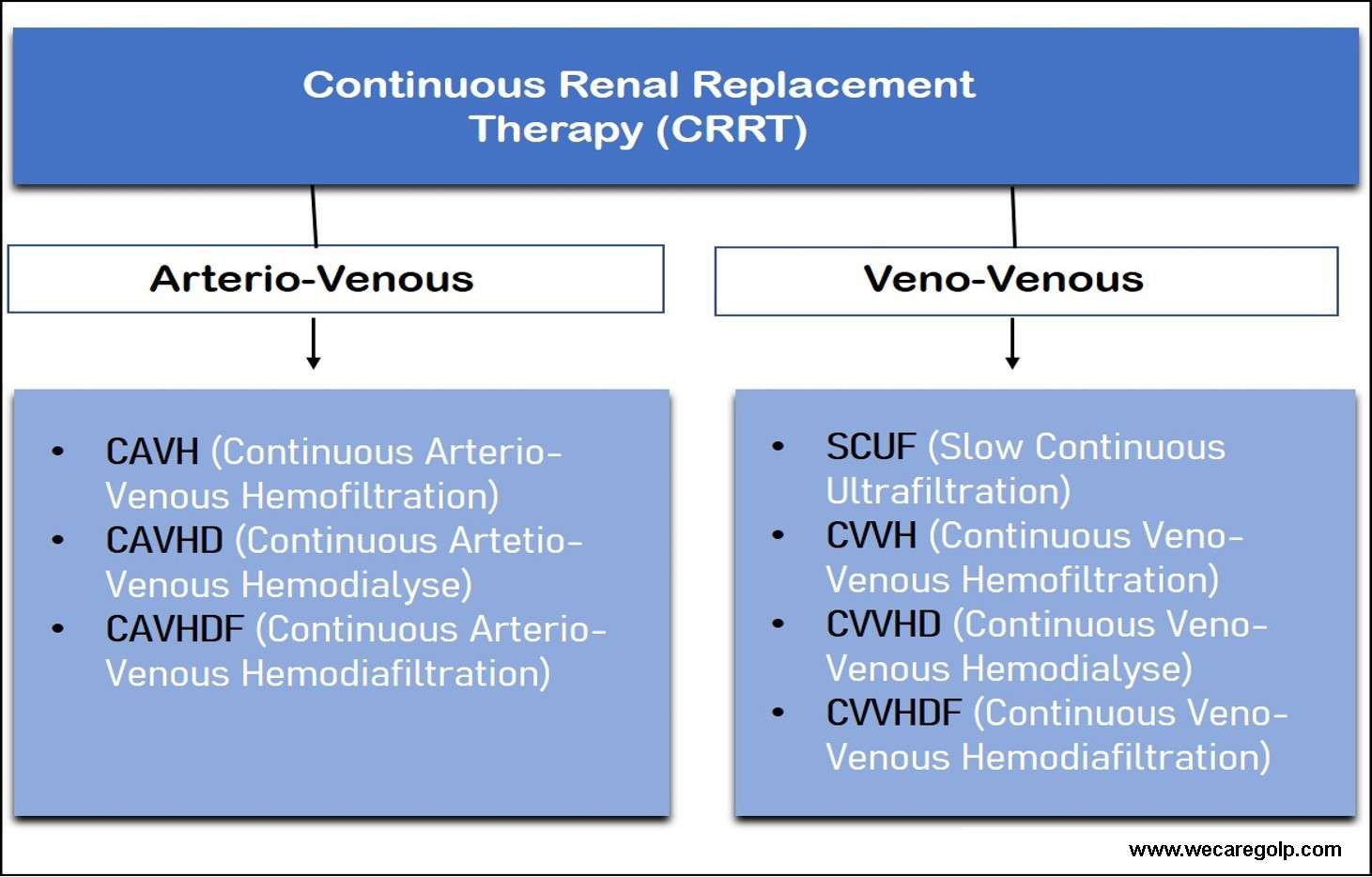
Bicarbonate in Bicarbonate Dialysis
Bicarbonate in Bicarbonate Dialysis There is a significant role of bicarbonate in bicarbonate dialysis. Two concentrates are used in bicarbonate dialysis: the so-called acid component and a bicarbonate solution (8.4%). Bicarbonate Buffer Hydrogen ions (H+) formed during metabolism are buffered to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which decomposes into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). Carbon dioxide … Read more