Diabetes Mellitus: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
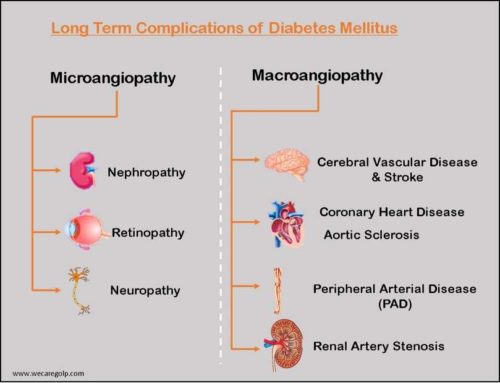
Introduction Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic condition characterized by increased blood glucose level, polyuria (excessive urine output), polydipsia (excessive thirst), and polyphagia (excessive hunger). If left untreated or uncontrolled may lead to serious damage to the heart, kidney, eyes, and blood vessels. Regulation of Blood Glucose in Healthy Condition Insulin Types of Diabetes … Read more