Antihypertensive Drugs are a group of drugs used to treat high blood pressure (Hypertension).
Hypertension
- Hypertension (HTN) (also known as systemic arterial hypertension) is indicated by persistently high blood pressure (BP) in the systemic arteries. Blood pressure is expressed as the ratio of systolic pressure (the pressure that blood exerts on the walls of arteries when the heart contracts) to diastolic pressure (the pressure when the heart relaxes).
- According to the world health organization (WHO), “Hypertension is a condition where the systolic blood pressure reading is ≥140 mmHg and (or) the diastolic blood pressure reading is ≥ 90 mmHg when it is measured on two different days.”
- Hypertension is a common cardiovascular disorder resulting in a major public health challenge to the population in socioeconomic and epidemiological transition.
- It is a leading cause of premature death worldwide and also a serious medical condition that increases the risk of heart, kidney, and other diseases.
Classification of Hypertension
Primary hypertension
- Primary hypertension (also called essential hypertension) is a type of hypertension that does not have an identifiable cause.
- It is the most common form of hypertension. About 90% of the affected people belong to this category.
Secondary hypertension
- Hypertension having a defined cause is known as secondary hypertension (remaining 10%).
- The various known causes of secondary hypertension can be kidney disease, vascular diseases, toxins, endocrine hypertension, gestational hypertension, etc.
Categories of Blood Pressure
The new categories of blood pressure (BP) according to the American Heart Association are shown in the figure below.
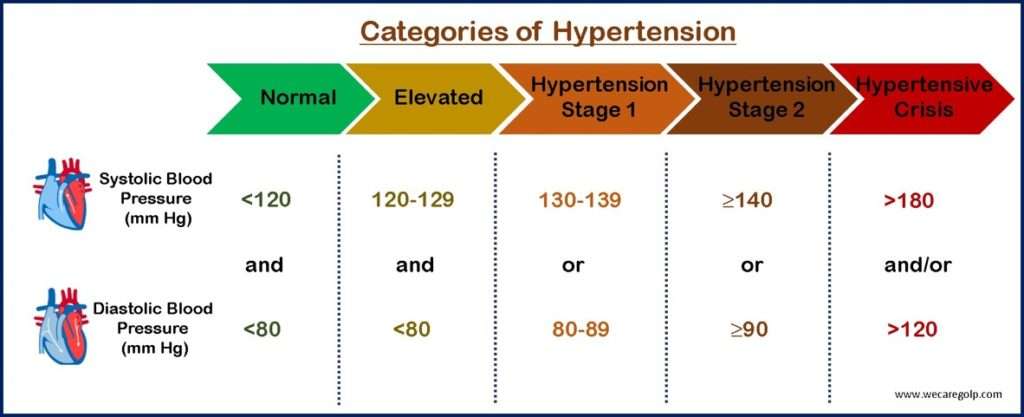
These categories should not be based on BP readings at a single point in time but rather should be confirmed by two or more readings (averaged) made on at least two separate occasions.
Complications of Hypertension
- Stroke
- Vision loss
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- Kidney failure
- Sexual dysfunction
Importance of Antihypertensive Drugs
One should adhere to antihypertensive drug because of following advantages.
- It reduces cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
- It helps maintain blood pressure at a healthy level.
- It keeps your heart from becoming overworked.
- It minimizes the impact of other associated Cardiovascular risk factors.
Types of Antihypertensive Drugs
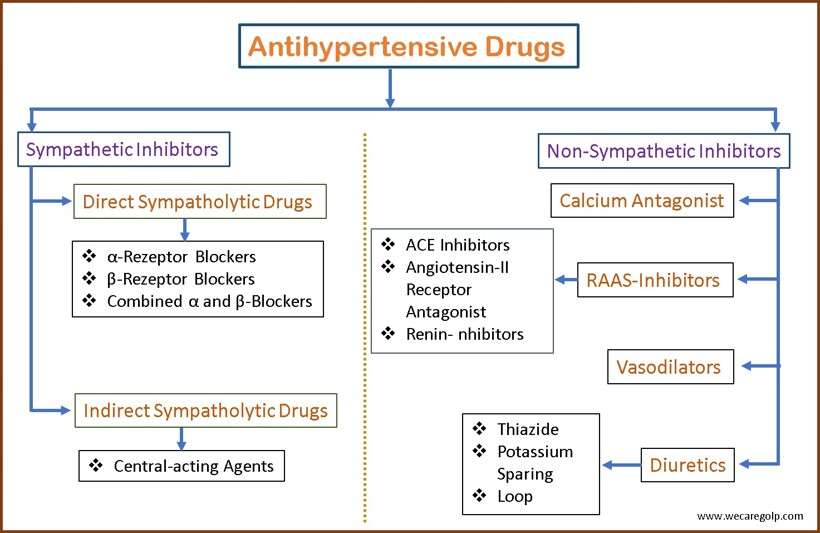
Sympathetic Inhibitors
Direct Sympatholytic Drugs (Adrenergic Receptor Antagonist)
These drugs relax the muscle tissue in the blood vessels and improve blood flow.
Alpha (α)-receptor blockers
- Hypertension
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Pheochromocytoma
- Heart failure
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
Pharmaceuticals
- Doxazocin (cardural, Doxadura)
- Prazosin (Minipress)
- Terazocin (Avanafil,tadalafil)
Indications
- Hypertension
- Benign prostate hyperplasia
- Pheochromocytoma
- Heart failure
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
Contraindications
- Cataract surgery
- Breastfeeding mother
- Kidney diseases
- Respiratory infection
Side effects
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Pounding Heartbeat
- Weakness
Beta (β)-receptor blockers
- It works by blocking the effect of the epinephrine hormone (adrenaline)
- It causes the heart to beat more slowly and reduces the heart rate, heart workload, and heart’s output of blood which in turn lowers the blood pressure.
Pharmaceuticals
- Atenolol (amiodarone,disopyramide)
- Metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol XL)
Indications
- Hypertension
- Angina pectoris
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Heart failure
- Myocardial infarction
- Tachycardia
Contraindications
- Peripheral vascular diseases
- Diabetes mellitus
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Asthma
Side Effects
- Feeling tired, dizzy, or light-headed
- Cold finger or toes
- Difficulties sleeping
Combined α- and β-blockers
- Stimulation of alpha and beta receptors can lead to the constriction of blood vessels causing increased blood pressure.
- β-blockers with α activity bind to α-1 and β-receptors and prevent their stimulation leading to the dilation of blood vessels.
- These drugs are administered via the IV route for the patient experiencing a hypertensive crisis.
Pharmaceuticals
- Carvedilol (Coreg),
- Labetolol (Trandate)
- Dilevalol (Unicard)
Indications
- Hypertension
- Hypertensive emergency
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity
Side Effects
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Nausea
- The tingling sensation on the scalp
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling and itching
Indirect Sympatholytic Drugs
- These drugs block the release and action of endogenous catecholamines in the sympathetic nervous system.
- It makes the heart beat slower and relaxes the blood vessels leading to decrease blood pressure.
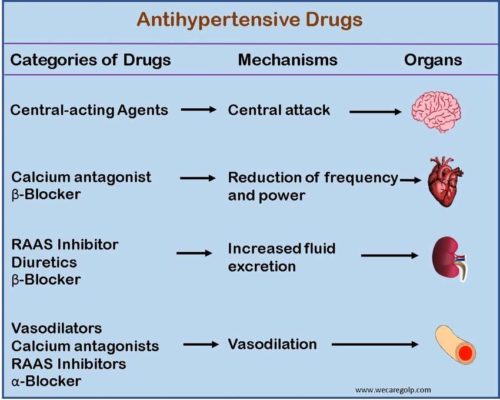
Central-acting agents
- It blocks signals from the brain to the nervous system that increase blood vessel ability to tense up or contract.
- Consequently, blood flows more easily to the veins and arteries, and blood pressure decreases.
Pharmaceuticals
- Alpha methyldopa (Aldomet, Dopamet).
- Clonidine Hydrochloride (Catapres,Kapvay).
Indications
- Attention deficit hyperactive disorder (ADHD)
- Tourette syndrome
- Drug withdrawal
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity
Side Effects
- Dry mouth
- Drowsy
- Bradycardia
- Constipation
- Weak or dizzy
- Gastric upset
Non-Sympathetic Inhibitors
Calcium antagonist
- It prevents the entry of calcium to the smooth muscle cells of the heart and arteries as calcium acts as muscle contraction.
- This drug relaxes and opens narrowed blood vessels, reduces heart rate, and decreases blood pressure.
Pharmaceuticals
- Amlodipine (Norvasc®)
- Diltiazem (cardiazem®,Tiazac®)
Indications
- Hypertension
- Angina
- Arrhythmia
- Migraine
Contraindications
- Severe hypotension
- Acute myocardial infarction
- Pulmonary congestion
- Sick sinus syndrome
Side Effects
- Constipation
- Dizziness
- Palpitation
- Fatigue
- Flushing
- Headache and Nausea
- Rash
RAAS (Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System) Inhibitors
RAAS inhibitors are a group of drugs that act by inhibiting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system directly.
ACE inhibitors
- ACE inhibitors help the body produce less angiotensin II which helps the blood vessels relax and open and lower the blood pressure.
Pharmaceuticals
- Enalapril (Vasotec)
- Lisinopril (Prinivil,Zestril)
- Quinapril (Accupril)
- Ramipril (Altace)
Indications
- Hypertension
- Coronary artery diseases
- Heart failure
- Diabetes
- Certain kidney diseases
- Heart attack
- Migraine
Contraindications
- History of angioneurotic edema
- Pregnancy
- Renal artery stenosis
Side Effects
- Dry cough
- Hyperkalemia
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Loss of taste
Angiotensin II receptor antagonist (Sartans)
- These drugs block the receptors so that the angiotensin II fails to constrict the blood vessels
- Blood vessels remain open, and blood pressure gets reduced.
Pharmaceuticals
- Telmisartan (Micardis)
- Valsartan (Diovan, Exforge)
Indications
- Hypertension
- Congestive heart failure
- Diabetic nephropathy
Contraindications
- Pregnancy
- Very low systematic blood pressure (systolic less than 80mm of Hg)
- Angioedema or anuric renal failure during previous drug exposure.
Side Effects
- Headache
- Fainting
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Respiratory symptoms
- Vomiting and Diarrhea
- Leg swelling
Renin inhibitors
- It inhibits the activity of renin which is responsible for stimulating angiotensin II formation.
- Angiotensin II is responsible for vasoconstriction, stimulation of aldosterone, and the renal retention of sodium and water.
- Thus, blood flows smoothly by reducing the heart´s workload and blood pressure decrease.
Pharmaceuticals
- Aliskiren (Rekturna,Rasilez)
Indications
- Hypertension
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity
- Pregnancy
- Recurrent treatment with ACE inhibitors or ARBs
Side Effects
- Nausea & vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Hyperkalemia
- Severe hypertension & headache
- Angioedema
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Hyponatremia
- Hyperuricemia
- Anaphylaxis
- Renal stone
- Chest pain
- Headache & tiredness
Diuretics
- Diuretics help get rid of excess sodium (salt) and water.
- It decreases the amount of fluid flowing through veins and arteries. As a result, blood pressure reduces.
Pharmaceuticals
- Thiazide diuretics
- Chlorthalidone (Thalidon, Thalidax)
- Hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide, Hydrodiuril)
- Potassium sparing diuretic-
- Amiloride hydrochloride (Midamor)
- Spironolactone (Aldactone)
- Loop diuretics
- Furosemide (Lasix, Furoscix)
Indications
- Heart failure
- Live failure
- Tissue swelling
- Certain kidney disorders, such as kidney stone
Contraindications
- Hypokalemia
- Severe hyponatremia
- Hypotension
- Azotemia
- Oliguria/anuria
- Hepatic coma
Side Effects
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Dehydration
- Muscle cramps
- Impotence
- Joint disorder
Vasodilators
- Vasodilators relax the wall of the blood vessel allowing the blood vessel to dilate and blood to flow easily through the vessels.
- The heart does not have to pump hard which reduces the blood pressure.
Pharmaceuticals
- Hydralazine (Apresoline, Hydre-zide)
- Minoxidil (Lonoten, Minodyl)
Indications
- Hypertension
- Pre-eclampsia or eclampsia
- Heart failure
- Pulmonary Hypertension
Contraindications
- History of angioedema
- Mitral valve rheumatic heart disease
- Right ventricular infarction
- Hypotension
- Severe hypersensitivity
Side Effects
- Tachycardia
- Heart palpitation
- Edema
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Excessive hair growth
- Joint pain
- Chest pain
Safe Antihypertensive Drugs in Pregnancy
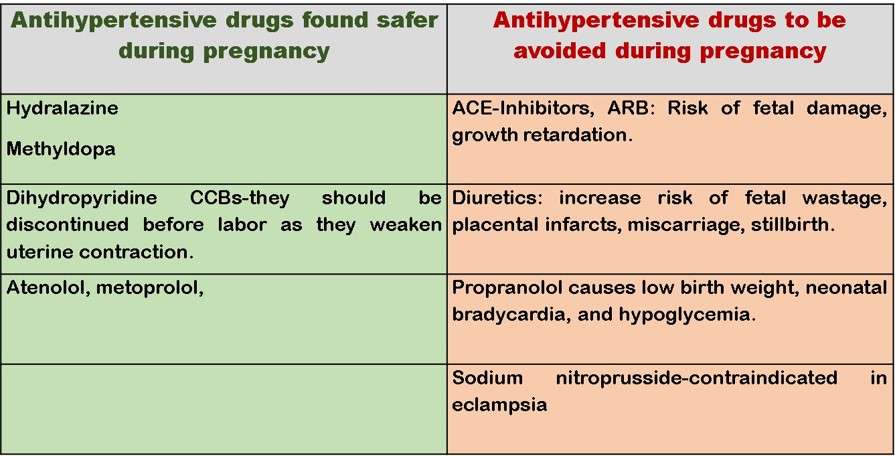
- Thus, antihypertensive drugs help to lower high blood pressure and keep the heart from being overworked.
- High blood pressure is also known as a “silent killer.”
- A careful selection of drug therapy followed by regular blood pressure monitoring and follow-up offers the best prospect to reduce the burden of morbidity and mortality in hypertension.
- One should strictly adhere to antihypertensive therapy to keep the heart healthy and reduce the risk of heart disease, heart attack, and stroke.
REFERENCE
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension
- https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/hypertensionaha.106.075895
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/21811-antihypertensives

Very informative! Hope to see more content from you
Sure. Do follow us, thank you!