Introduction
CT scan (or Computed tomography scan) is a computerized x-ray imaging technique in which a narrow beam of x-rays is focused on a person and rotated quickly around the body that produces signals that are processed by the computer to create cross-sectional tomographic images (slices). CT scans are also called Computed Axial Tomography (CAT) scans. The series of X-rays and a computer is used to generate 3 dimensional (3D) images of soft tissues and bones. The scanner uses a thin beam of radiation to scan from different angles of the body. It then provides the scanned images to a computer that creates separate cross-sections or slices, of the internal body.
Indications of CT Scan
CT scan is a crucial diagnostic procedure specially performed for diagnosing different illnesses and analyzing injuries. Some of the indications for CT scans are as follows:
- To diagnose muscle disorders, bone fractures/deformities, and infections
- To spot the location of tumors, lesions including cancer
- To examine the internal structures of the body and blood vessels
- To determine the extent of internal injuries and bleeding/hematoma
- To guide various procedures like biopsies and surgeries
- To evaluate the effectiveness of treatments for certain medical/surgical conditions, including heart disease and cancer
Advantages of CT Scan
- CT scanning procedure is painless, noninvasive, and has high accuracy.
- It can simultaneously produce images of blood vessels, soft tissue, and bone.
- It provides very detailed images than a conventional x-ray or Ultra sonogram.
- The imaging procedure is fast and simple. So it is very effective in emergency cases, to reveal internal bleeding and injuries thus helpful in saving lives.
- A CT scan is affordable for a variety of clinical issues.
- It is less sensitive to the movement of the patient than MRI.
- It can be done in patients with any kind of implanted medical device.
- It provides real-time imaging that guides needle biopsies and aspirations involving the lungs, liver, abdomen, pelvis, bones, etc.
- It helps in diagnosis and thus decreases the need for diagnostic/exploratory surgery and biopsies.
- Radiation is not retained in a patient’s body after a CT scan.
Types of CT Scan
Spiral CT
- Spiral CT or helical CT is the scanning method in which the entire X-ray tube revolves around the middle axis of the body area being scanned.
- The drawback of this type of CT is the weight and passivity of the equipment which limits the spinning speed of the equipment.
- Some designs of machines use two X-ray sources and a detector range neutralized by an angle, as a method to improve temporal resolution.
Electron beam tomography (EBT)
- EBT is a particular form of CT scan in which a large X-ray tube is made so that only the pathway of the electrons, traveling between the electrodes (cathode and anode) of the X-ray tube, is rotated using deflection coils.
- Its major advantage is that sweep speeds can be faster, allowing for clear imaging of mobile structures, such as the heart and blood.
Dual-source CT
- Two X-ray tube detector system is used in dual-source CT, whereas conventional CT uses only one tube. It is a modern and sophisticated type of scan.
- This scanner permits quick scanning with a higher temporal resolution by obtaining a complete CT slice in just half rotation.
- Fast imaging also reduces blurring due to motion, and high heart rates and is beneficial for ill patients who have difficulty holding their breath or who can’t take heart-rate-decreasing medication.
CT perfusion imaging
- CT perfusion imaging is a specific form of CT to assess the flow of blood, blood circulates time, and blood volume of an organ, by injecting a contrast agent.
- This is useful to detect poor brain perfusion and stroke in the brain better than a conventional spiral CT scan.
Contraindications of CT Scan
- Pregnancy: can be done if the benefits of the test overweigh the potential risks
- Known history of iodine allergy
- Hypothyroidism or an enlarged thyroid gland
- Planned radioiodine treatment of thyroid cancer
- Gastrointestinal perforation (for oral or rectal dye/solutions)
Procedure of CT Scan
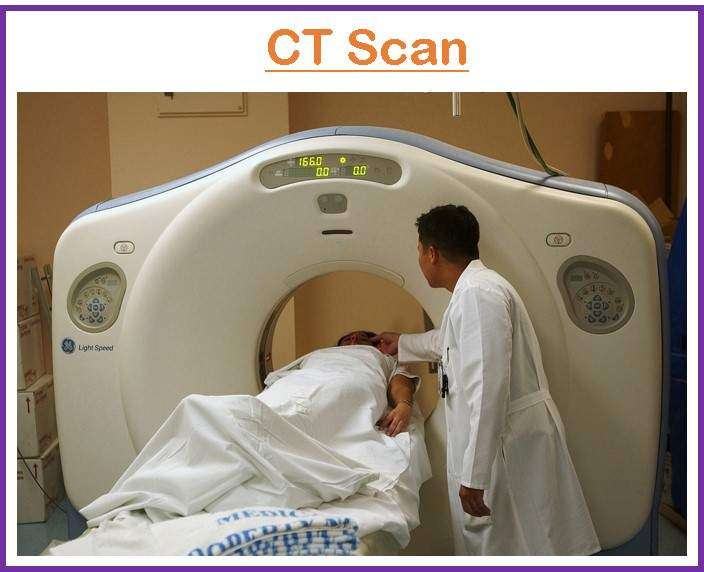
Before the Procedure
- Patients need to wear a hospital gown and remove all metal objects including jewelry from the body.
- Contrast agent: Contrast agents help soft tissue to appear clearly by blocking the X-rays. Thus, they appear white on the scan, highlighting organs, blood vessels, liver, gallbladder, or other structures.
- Contrast materials are usually made of iodine or barium sulfate and can be given via oral, intravenous route, or as Enema.
- Oral contrast material enhances scans of the digestive tract and enemas are given to visualize intestines.
- The patient may need to withhold oral feedings a few hours before the scan requiring a contrast agent.
- Some patients are advised to take plenty of fluids before and after the procedure to remove the contrast material from the body via the kidney.
- If a patient has diabetes and is taking metformin, it must be held 24 hours before and 48 hours after the procedure or as prescribed by the doctor.
- Children who cannot stay calm may require sedatives during the procedure.
During the Procedure
- The patient must lie flat on the scanner table. Straps and foam pillows may be used to position and help keep the body still.
- The table is slid into the cylindrical hole of the machine.
- The patient will be asked to remain still and hold his breath frequently during the procedure.
- The patient can communicate with the technologist in case of difficulties like breathing problems, palpitation, sweating, etc.
- Many images are taken depending on the condition or indication and part of the body.
- The equipment makes clicks and buzzes while taking the images which is normal.
- It may take a few minutes to half an hour or more according to the type of scan.
After the Procedure
- The person may need to stay in the diagnostic center for a brief period if s/he has received the iodinated contrast material or sedation during the procedure.
- A follow-up appointment is done with a consultant physician or surgeon regarding the report of the scan and further management of the illness.
Precautions of CT Scan
- Allergic reactions to contrast dyes: Usually the reaction is mild with itchiness or rashes but in a few cases, the dye may trigger a life-threatening reaction. A history of allergies to medications, seafood, or iodine should be explored before the procedure.
- Rarely contrast materials can lead to kidney problems. So the history of any kidney problems should be explored before the CT scan.
Interpretation
The presentation of tissues on a CT scan is expressed in terms of ‘density.’
- Darker structures like air, fat, and cerebrospinal fluid are black (hypodense or low density).
- Brighter structures like bone, calcification, and contrast are white (hyperdense or high density).
- Brain tissues are grey (isodense).
- Blood can be confusing because its appearance differs according to its duration.
- Acute blood is hyperdense
- Subacute blood is isodense
- Chronic blood (after many weeks old) is hypodense
Summary
- A computerized tomography (CT) scan merges a series of X-ray images taken from various angles around the body and computer processing is done to create slices (cross-sectional images) of the bones, soft tissues as well as blood vessels of the body.
- A CT scan is very useful in urgent cases for those who may have internal injuries from accidents or other types of trauma.
- A CT scan can visualize almost whole part of the body and is utilized to diagnose diseases to plan various medical, surgical, and/or radiation treatments.
- There are a few risks associated with CT scans like radiation exposure and allergies to contrast agents.
References
- Patel, P. R., & Jesus, D.O. (2022). CT Scan. StatPearls Publishing. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33620865/
- Goldman, L.W. (2007, Sep). Principles of CT and CT Technology. Journal of Nuclear Medicine Technology, 35 (3) 115-128; DOI: https://doi.org/10.2967/jnmt.107.042978
- Zainab T. et al (2020). A critical review of medical imaging techniques (CT and PET scans) in the medical field. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 870 012043 DOI 10.1088/1757-899X/870/1/012043
- National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (2022). Computed-Tomography(CT) Scan. Retrieved on 2023, March 11from https://www.nibib.nih.gov/science-education/science-topics/computed-tomography-ct
- Cleveland Clinic. CT Scan. Retrieved on 2023, March 11 from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/4808-ct-computed-tomography-scan
- NHS.UK. (2021). CT Scan. Retrieved on 2023, March 08 from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/ct-scan/
- Weatherspoon, D. (2022). CT Scan. Healthline. Retrieved on 2023, March 08 from https://www.healthline.com/health/ct-scan