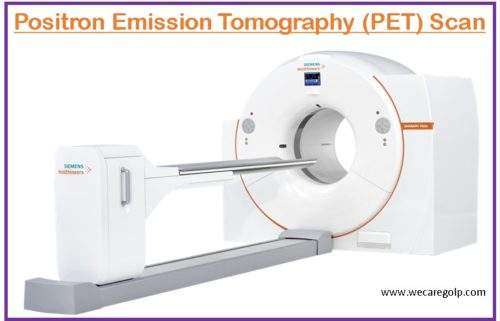
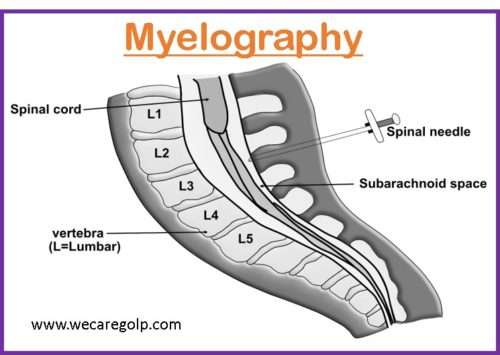
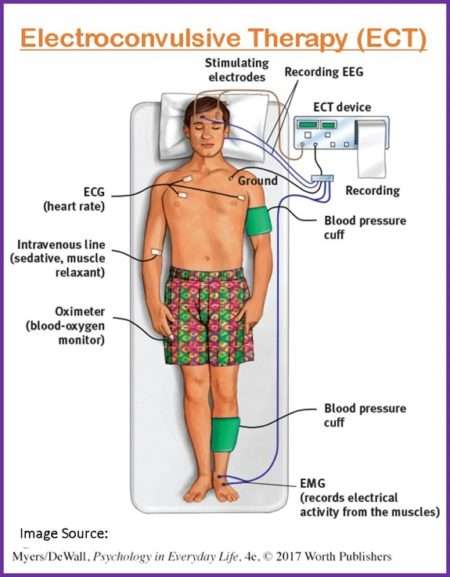
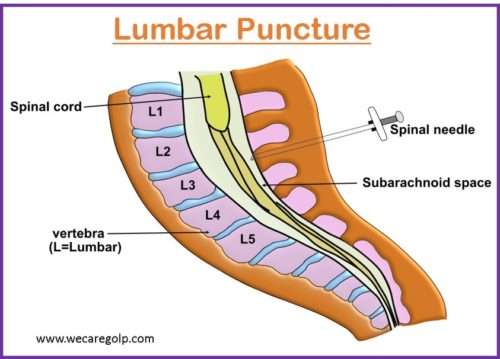
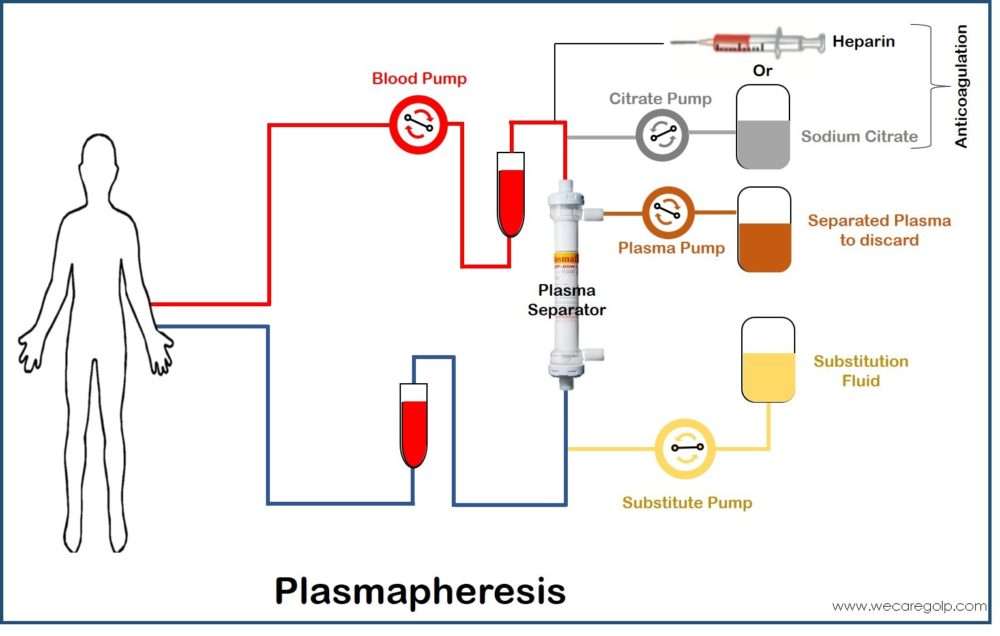
PET Scan (Positron Emission Tomography Scan)
Introduction PET scan (positron emission tomography Scan) is a functional scanning technique that uses radiotracers (radioactive substances), a special camera, and a computer to project and measure variations in metabolic processes, and other physical activities inside the body including blood flow, local chemical composition, as well as absorption. The scan reveals both normal and abnormal metabolic or biochemical activities of the tissues and … Read more